Mechanical Ventilation Is Necessary for a Trauma Patient With a
A 68-year-old patient with a history of smoking and emphysema b. Each lesion group of patients was matched with another group differing in the type of lesion according to gender age and weight.
Basically these involve burns in your respiratory system.

. This review examines the limited evidence for intraoperative ventilator practices during trauma surgery Most recommendations for surgical ventilator management are derived from ICU. Trauma patients may require mechanical ventilation secondary to respiratory center depression or the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDS. Hypercapnic respiratory failure due to a decrease in minute ventilation.
The BSE used mental status facial symmetry swallow reflex and oral ice chips and water to identify swallowing dysfunction. One of the most frequent intrathoracic injuries is lung contusion that results from blunt chest trauma. Invasive mechanical ventilation helps stabilize patients with hypoxemic and hypercapnic respiratory failure decreases inspiratory work of breathing redistributes blood flow from exercising respiratory muscles to other tissues in patients with shock and allows for the implementation of lung-protective low tidal volume ventilation in patients with acute.
On the other hand lung trauma needs to be treated on an individual basis depending on the. Which patient is most at risk for failure to wean and ventilator dependence. One end of the tube is inserted through the opening while the other is connected to a ventilator.
The primary indications for mechanical ventilation are1 Airway protection in a patient who is obtunded or has a dynamic airway eg from trauma or oropharyngeal infection. Particularly in patients with multiple traumas severe blunt chest injuries and especially pulmonary contusions may deteriorate the patients outcome due to increased morbidity and mortality. Identify risk factors for swallowing.
Clinical bedside swallowing evaluation BSE developed by our aspiration was defined as either a witnessed aspiration event institutional Speech and Language Department on trauma or suctioning of enteric material from below the vocal cords patients who require intubation and mechanical ventilation to during bronchoscopy. Up to 10 cash back Mechanical ventilation is an essential part of anesthesia for trauma surgery but there are few recommendations for intraoperative ventilator management. Penetrating wounds are most commonly caused by 27.
The complexity of injury in trauma patients makes it challenging to provide an optimal oxygenation while protecting the lung from further ventilator-induced injury to it. Patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome are an example of the type of patient likely to need this type of ventilation. Mechanical ventilation in a patient with both a brain injury and ALI requires a balance between the principles that guide brain injury and the mechanical ventilation required to be protective of the lung.
1 active humidification through a heated humidifier and 2 passive humidification through an HME. Mechanical ventilation is a treatment option for burn patients who have suffered a severe inhalation injury. Indications for mechanical ventilation with chest trauma include flail chest chest pain requiring large doses of respiratory depressant pain medications pulmonary contusion postoperative thoracotomy hemodynamic instability or severe associated injuries.
There are three types of HMEs or. For people who are unable to be weaned from the ventilator or are expected to require long-term mechanical ventilation a surgical procedure called a tracheostomy may be used to create an opening in the neck to bypass the mouth or nose. This is a 1-year 2008 prospective study of all adult trauma patients admitted to the intensive care unit requiring mechanical ventilation.
When a patient has noncompliant lungs with poor oxygenation PCV delivers a set rate of ventilations with a limit on the amount of pressure allowed. Typically inhalation injuries occur because of trauma that affects many of the bodys organ systems. Guidelines for noninvasive mechanical ventilation NIMV recommend continuous positive airway pressure in patients with thoracic trauma who remain hypoxic despite regional anesthesia.
Upon separation from mechanical all patients received a BSE. Hypoxemic respiratory failure due to a failure of oxygenation. Examples of blunt trauma are.
Often inhalation injuries are common in burn victims. A 57-year-old patient who experienced a cardiac arrest c. Parenchymal lung injuries such as pulmonary contusion may require.
That it is mandatory to humidify inspired gas during mechanical ventilation when an ET or tracheostomy tube is present1 Two systems are available for warming and humidifying gases delivered to patients who are mechanically ventilated. High PEEP can lead to elevated intrathoracic pressure which results in decreased cerebral venous drainage and therefore poor cerebral perfusion. Mechanical ventilation is necessary for a trauma patient with a n 24.
Settings are changedadjusted as needed until the patient achieves optimal ventilation Characteristics of ventilator modes Based on work of breathing the patient canshould perform- AKA inspiratory effort needed to overcome the elasticity. Head trauma patients usually require ventilator support due to respiratory failure secondary to impaired consciousness decreased respiratory drive chest injury or ARDS. We performed a retrospective study measuring the REE of critically ill patients with 3 different types of lesions trauma medical surgical who were treated with mechanical ventilation and sedation.
Ventilation may be required by patients in conditions that include. Understand traumas effects on students behavior with this free resource from CPI. Short-term ventilation while being under general anesthesia for a surgical procedure.
Flail chest is not an absolute indication for mechanical ventilation. Mechanical ventilation is a life-support treatment in the hospitals for critically ill people in acute respiratory distress or failure. The critical care charge nurse is responsible for the care of four patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
The treatment guidelines and protocols for trauma management course prepares physician and non-physician 25. In the case of these diseases associated with severe pain mechanical ventilation cannot only be. Chest trauma is one important factor for total morbidity and mortality in traumatized emergency patients.
Although usually administered with an endotracheal tube mechanical ventilation can be applied by. In case of isolated brain injury a degree of vulnerability is present in the lung tissue secondary to the proinflammatory state 19 20 21 This is aggravated by the use of high tidal volumes 22. These include cervical intervertebral disc disease and flail chest after thoracic trauma as well as post-operative hypoventilation following thoracotomy.
Ad A successful academic year incorporates these trauma-informed approaches from CPI.

Understanding Mechanical Ventilation A Practical Handbook Semantic Scholar
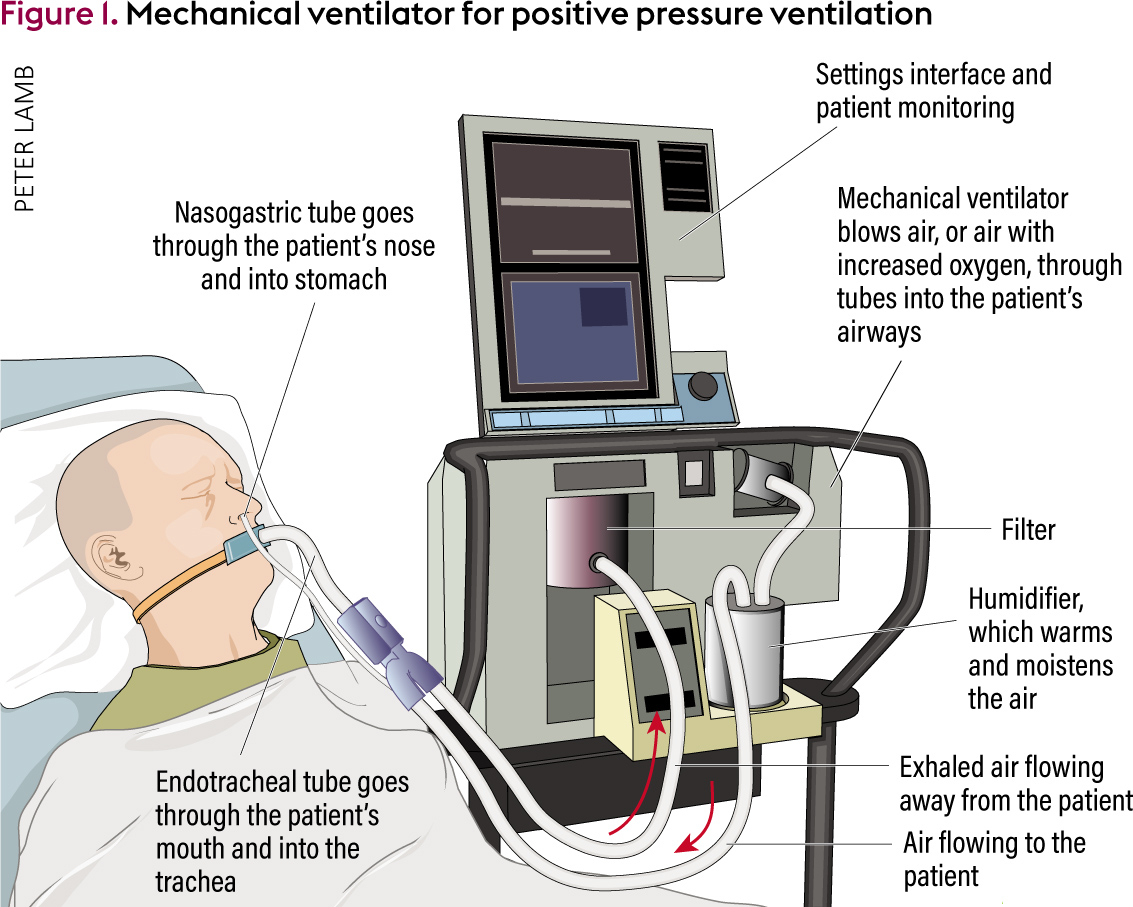
An Overview Of Mechanical Ventilation In The Intensive Care Unit

How Does A Ventilator Work Ids Medical Systems News Nursing Care Medical Nurse

No comments for "Mechanical Ventilation Is Necessary for a Trauma Patient With a"
Post a Comment